What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s Disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It develops gradually and can begin with a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. While tremors are the most well-known symptom, the disorder also commonly causes stiffness or slowing of movement. Understanding what Parkinson’s Disease is, its symptoms, causes, and diagnosis is essential for patients, caregivers, and anyone interested in neurological health.
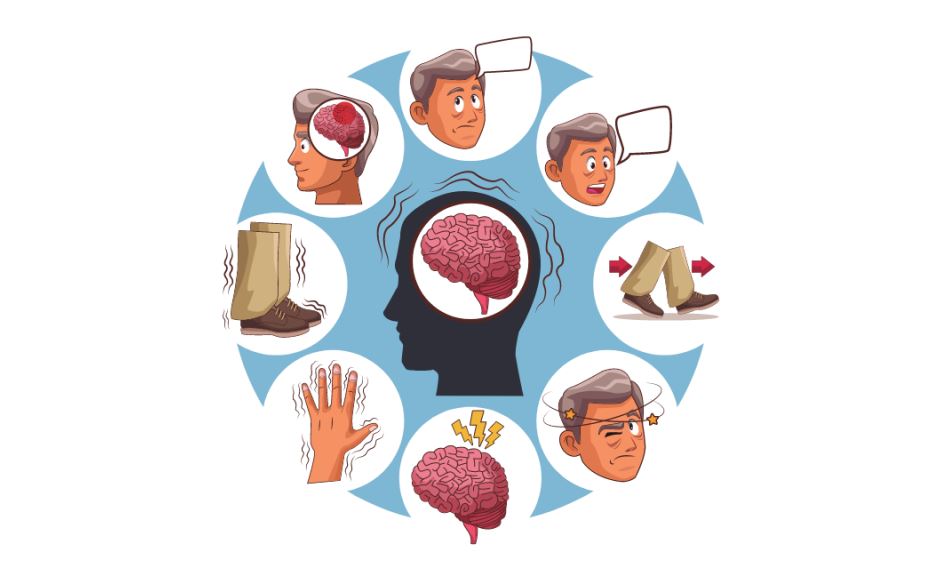
What Exactly is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a chronic and progressive movement disorder caused by the loss of dopamine-producing brain cells, particularly in the substantia nigra region. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in sending signals to control muscle movement. When dopamine levels decrease, the brain struggles to regulate body movements smoothly.
“Parkinson’s is not just a movement disorder; it affects many aspects of daily life and can have emotional and cognitive impacts.” — Mayo Clinic
Common Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Symptoms usually start subtly and worsen over time. The most common include:
- Tremor: Shaking, often beginning in a hand or fingers.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement, making simple tasks difficult.
- Muscle Rigidity: Stiffness in limbs and trunk that limits range of motion.
- Postural Instability: Impaired balance and coordination leading to falls.
- Speech and Writing Changes: Soft, slurred speech or smaller handwriting.

What Causes Parkinson’s Disease?
The exact cause of Parkinson’s Disease remains unknown, but research points to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some known contributors include:
- Genetic Mutations: Certain gene mutations increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to pesticides and toxins.
- Age: Risk increases with age, typically affecting people over 60.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop Parkinson’s than women.
For a deeper dive into causes and risk factors, visit our detailed article on Causes and Risk Factors of Parkinson’s Disease.
How is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed?
There is no single test to diagnose Parkinson’s Disease. Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on medical history and neurological examination. Doctors look for key symptoms like tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia. Imaging tests such as MRI or DAT scans may help rule out other conditions.
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. If you or a loved one experience symptoms, consult a neurologist promptly. Learn more about diagnosis methods in our article How Parkinson’s Disease is Diagnosed.

Living with Parkinson’s Disease
While Parkinson’s Disease currently has no cure, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgical options. Lifestyle adjustments, including exercise and nutrition, play a significant role in symptom management.
For practical tips on daily living and support, check out Living with Parkinson’s Disease.
Reliable Resources for Further Information
For trustworthy and up-to-date information, consider these reputable sources:
- Mayo Clinic – Parkinson’s Disease
- The Parkinson’s Foundation
- NIH – Parkinson’s Disease Information
- The Parkinson’s Disease Protocol
Staying informed and connected to reliable sources is key to navigating Parkinson’s Disease effectively.
