Treatment Options for Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a complex, progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement and motor control. Although there is currently no cure, a variety of treatment options for Parkinson’s have been developed to manage symptoms, slow progression, and improve patients’ quality of life. Understanding these treatment modalities is crucial for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers to create an individualized care plan that addresses both motor and non-motor symptoms effectively.
1. Pharmacological Treatments: Managing Dopamine Deficiency
The mainstay of Parkinson’s management is medication therapy aimed at replenishing dopamine or mimicking its effects. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating movement, and its deficiency leads to the characteristic symptoms of Parkinson’s.
- Levodopa (L-DOPA): This is the most effective medication for relieving motor symptoms. Levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier and converts into dopamine, helping to restore normal movement. It is typically combined with carbidopa to prevent premature conversion outside the brain and reduce side effects such as nausea.
- Dopamine Agonists: Drugs like pramipexole, ropinirole, and rotigotine directly stimulate dopamine receptors. They may be used alone in early disease or alongside levodopa in advanced stages to smooth out motor fluctuations.
- Monoamine Oxidase B (MAO-B) Inhibitors: Selegiline and rasagiline inhibit the enzyme that breaks down dopamine, prolonging its availability and mildly improving symptoms.
- Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT) Inhibitors: Entacapone and tolcapone block the COMT enzyme, extending the effect of levodopa and reducing “off” periods when medication effects wear off.
- Anticholinergics: These medications help control tremors but are less commonly used due to side effects like confusion and dry mouth, especially in older adults.
- Amantadine: Originally an antiviral, amantadine can reduce dyskinesias (involuntary movements) caused by long-term levodopa use.
While medications are effective, long-term use of levodopa can lead to motor complications such as dyskinesias and wearing-off phenomena, requiring careful dose adjustments and combination therapies.
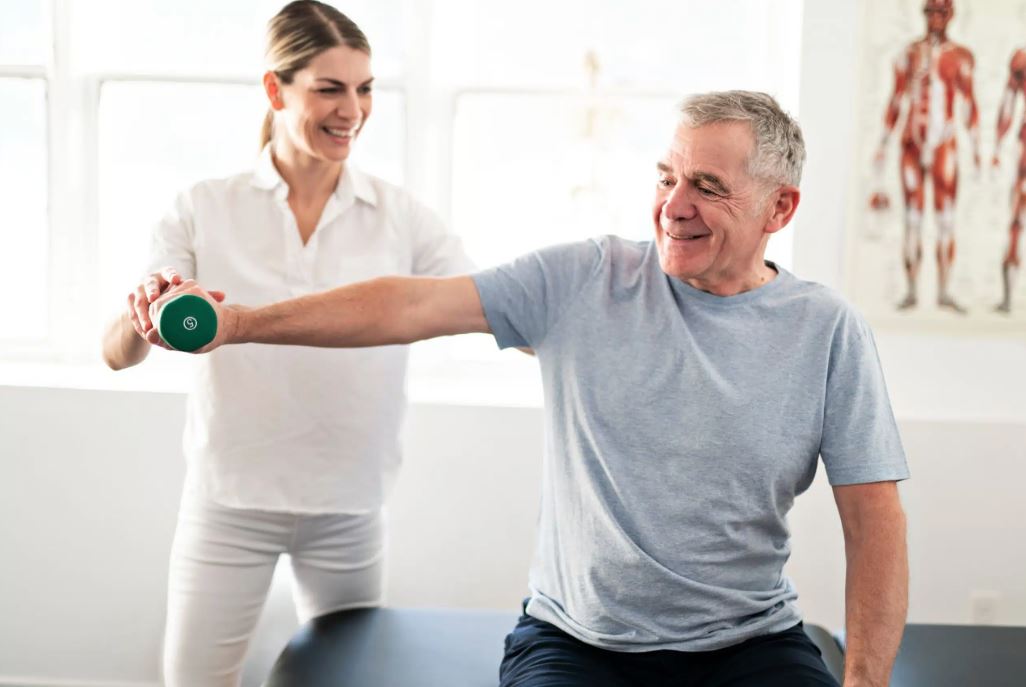
2. Non-Pharmacological Therapies: Enhancing Function and Quality of Life
Alongside medications, various therapies help maintain and improve physical function, communication, and daily living skills.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercise programs improve muscle strength, flexibility, balance, and gait. Techniques such as treadmill training, cueing strategies, and balance exercises help reduce freezing of gait and falls.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps patients adapt their environment and daily activities to maintain independence. Therapists recommend assistive devices and strategies to overcome challenges with fine motor skills and daily tasks.
- Speech and Language Therapy: Addresses speech difficulties like soft voice, slurred speech, and swallowing problems. Techniques include voice exercises and swallowing maneuvers to improve communication and reduce aspiration risk.
- Psychological Support: Counseling and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) help manage depression, anxiety, and cognitive changes often associated with Parkinson’s.

3. Surgical Interventions: Advanced Treatment Options
When medications no longer adequately control symptoms or cause significant side effects, surgical options may be considered.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): DBS is the most common surgical treatment for Parkinson’s. It involves implanting electrodes in specific brain areas such as the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus interna. These electrodes deliver controlled electrical impulses that regulate abnormal brain activity, leading to improved motor function and reduced medication needs.
- Lesioning Procedures: Surgeries like pallidotomy or thalamotomy create small lesions in brain regions involved in motor control to alleviate symptoms. These are less common now due to the reversibility and adjustability of DBS.
- Experimental and Emerging Therapies: Research is ongoing into gene therapy, stem cell transplantation, and novel neuroprotective agents that aim to modify disease progression rather than only treat symptoms.
“Deep Brain Stimulation represents a breakthrough for patients with advanced Parkinson’s, offering significant symptom relief and improved quality of life.” — Parkinson’s Foundation
4. Lifestyle and Complementary Approaches
Lifestyle changes and complementary therapies can support medical treatments and promote overall well-being.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in aerobic activities, strength training, yoga, tai chi, and dance improves mobility, balance, mood, and cardiovascular health.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, fiber, and adequate hydration supports brain health and digestive function, which can be affected in Parkinson’s.
- Stress Reduction: Mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques help manage anxiety and improve sleep quality.
- Support Networks: Participation in support groups and Parkinson’s communities provides emotional support, education, and coping strategies.

5. Monitoring and Personalized Care
Parkinson’s Disease symptoms and medication responses vary widely among individuals. Regular follow-up with neurologists or movement disorder specialists is essential to monitor disease progression, adjust treatments, and manage complications such as cognitive decline or autonomic dysfunction.
A multidisciplinary approach involving doctors, therapists, nurses, and caregivers ensures comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s evolving needs.
Related Articles on 2thealth.com
To deepen your understanding of Parkinson’s Disease and its management, explore these related articles:
- How Parkinson’s Disease is Diagnosed
- Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
- Living with Parkinson’s Disease
- The Parkinson’s Disease Protocol
